Camera Communication Architecture
This page explains the OV20i's dual-tier communication design and how native industrial protocols work alongside Node-RED extensible communication capabilities.
Communication Architecture Overview
Two-Tier Communication Design
The OV20i implements a sophisticated communication architecture with two distinct layers:
Communication Tiers:
- Native Industrial Protocols - System-level built-in communication (Profinet, Ethernet/IP)
- Node-RED Extensible Protocols - Recipe-specific communication capabilities (MQTT, Modbus, TCP, HTTP)
Communication Scope and Control
System vs Recipe Level:
- System-level protocols apply globally across all recipes
- Recipe-level protocols are unique to each specific inspection workflow
- Configuration location determines communication scope and behavior
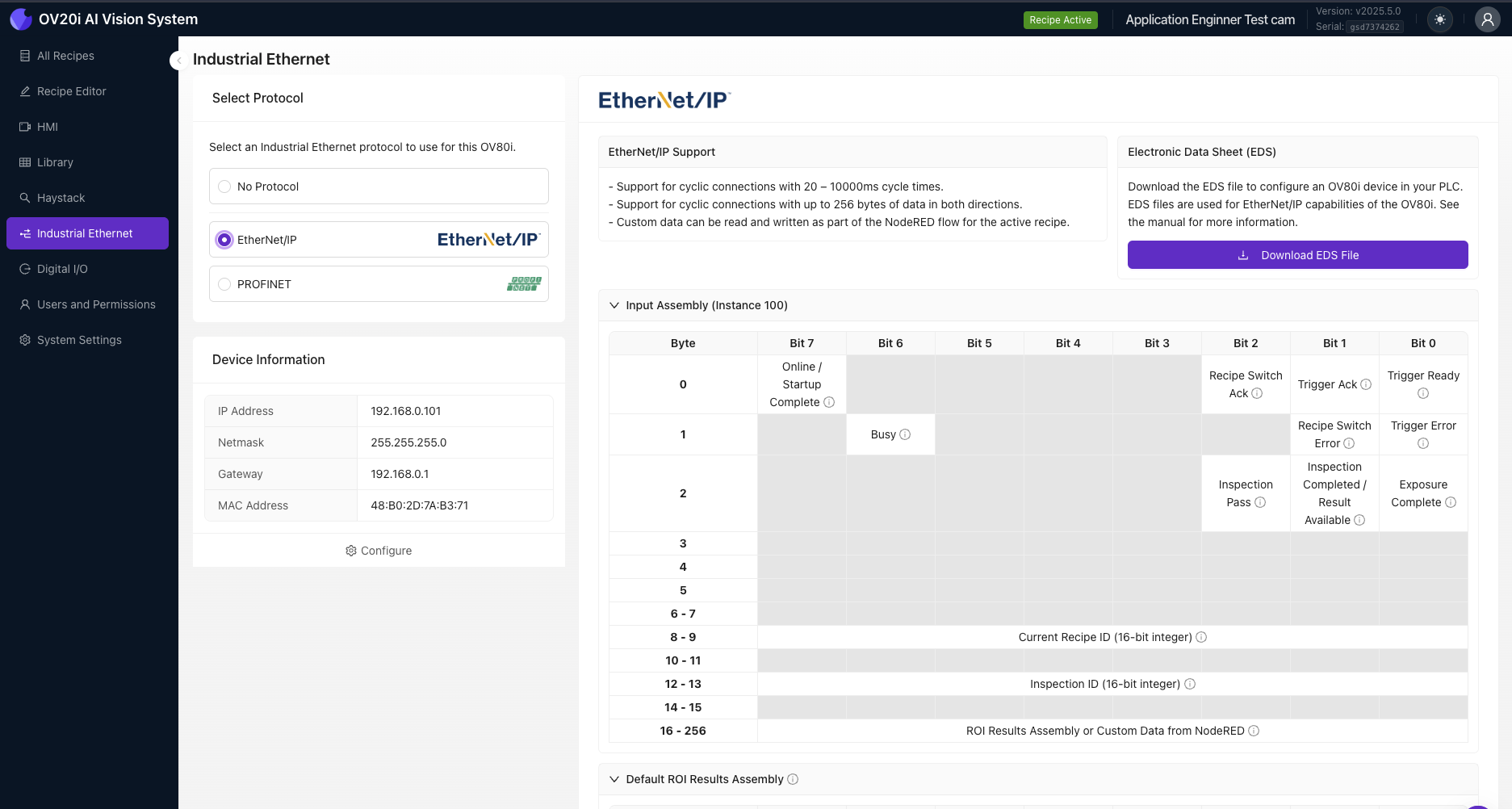
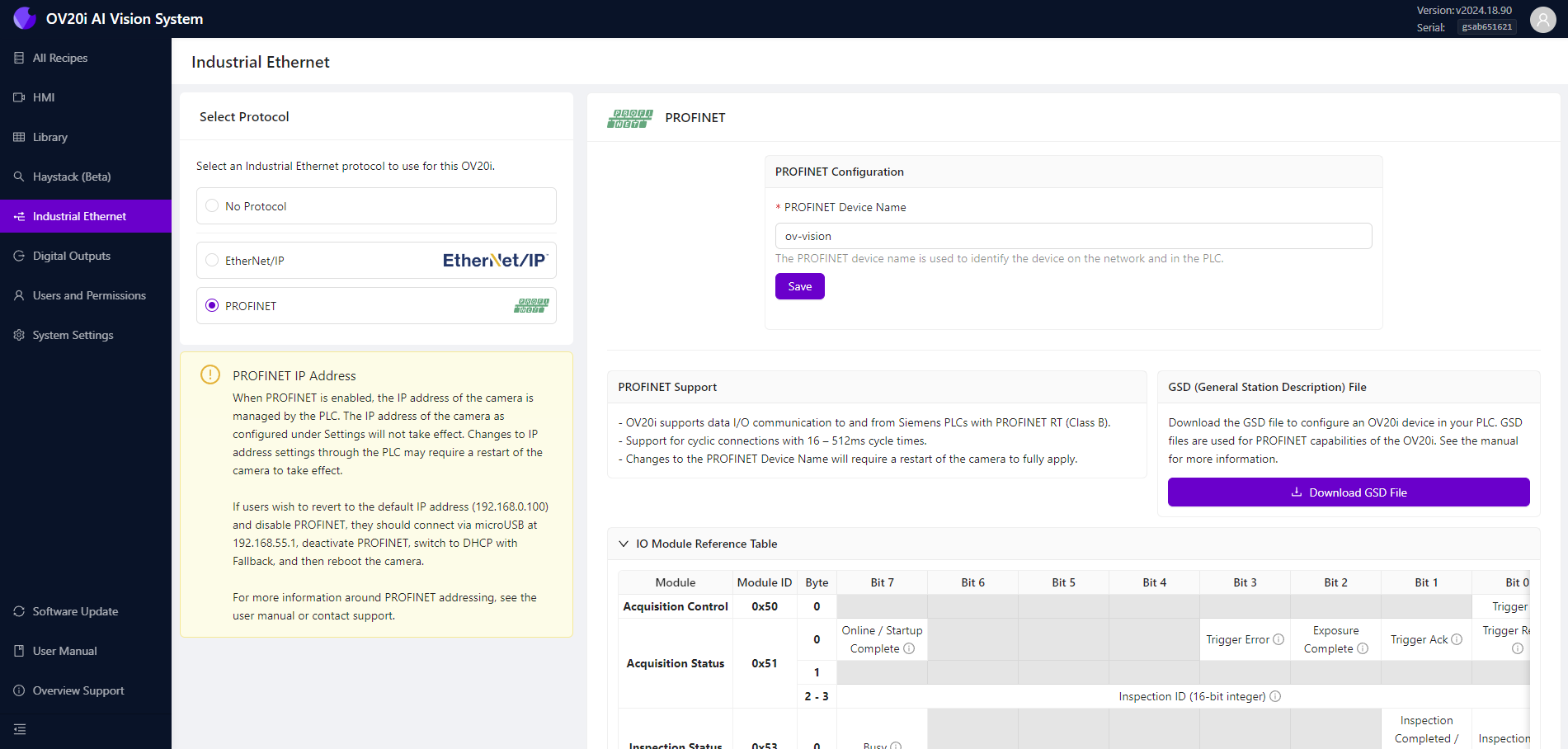
Native Industrial Communication
Built-in PLC Protocols
Camera System-Level Configuration:
- Profinet & Ethernet/IP - Only communication protocols configured at camera system level
- Direct Integration - No additional programming or Node-RED flows required
- Industrial Standards - Native support for major automation platforms (Siemens, Allen-Bradley, Mitsubishi, Omron)
- Bidirectional Data Exchange - Trigger commands, status feedback, recipe control, inspection results
Key Characteristics:
- Global Scope - Configuration affects all recipes
- System Settings - Managed through camera system configuration, not Node-RED
- Immediate Response - Direct hardware-level communication
- Industrial Reliability - Built for factory automation environments
References: Triggering Modes, System Settings Architecture
Node-RED Extensible Communication
Recipe-Level Protocol Flexibility
Node-RED Flow-Based Protocols:
- MQTT - IoT messaging and cloud integration via Node-RED flows
- Modbus - Industrial device communication through Node-RED nodes
- TCP - Custom protocol implementation for specialized systems
- HTTP - Bidirectional web service communication
Recipe-Specific Characteristics:
- Custom Logic - Each recipe defines its own communication workflows
- Protocol Selection - Choose appropriate protocols for specific inspection requirements
- Integration Flexibility - Connect to databases, cloud services, custom applications
- Data Processing - Transform and route inspection data as needed
References: Node-RED Basics, System Settings Architecture
HTTP Communication Duality
Inbound HTTP (Camera as Server):
- Open API Endpoints - External systems can trigger inspections remotely
- Recipe Management - Remote recipe switching and control via HTTP requests
- System Control - External applications can control camera functions
- Real-time Access - Immediate response to external HTTP requests
Outbound HTTP (Camera as Client):
- Node-RED HTTP Nodes - Camera initiates communication to external web services
- Custom Integration - Recipe-specific web service communication
- Data Publishing - Send inspection results to external systems and databases
- Third-party Integration - Connect to MES, ERP, and cloud platforms
Communication Flow Architecture
System-Level vs Recipe-Level Communication
Camera System Communication:
- Global Configuration - Profinet/Ethernet/IP settings apply to entire camera
- Network Foundation - IP addressing, subnet configuration affects all communication
- Built-in Protocol Support - No programming required for industrial integration
- Cross-Recipe Consistency - Same communication behavior regardless of active recipe
Recipe-Specific Communication:
- Unique Workflows - Node-RED flows are specific to each recipe
- Protocol Customization - Different recipes can use different communication methods
- Application Logic - Communication behavior tailored to inspection requirements
- Data Transformation - Recipe-specific data processing and routing
Communication Response Hierarchy
Immediate Response Tier:
- Digital I/O Signals - Hardware-level immediate response
- Native PLC Protocols - Direct industrial communication
Programmed Response Tier:
- Node-RED Flows - Custom logic and protocol handling
- Data Processing - Inspection result transformation and routing
External Integration Tier:
- HTTP Endpoints - Web service integration and external control
- Cloud Communication - MQTT and internet-based protocols
Integration Patterns and Strategies
Hybrid Communication Architectures
PLC + Node-RED Pattern:
- Native PLC for immediate triggers and status feedback
- Node-RED flows for data routing, logging, and advanced integration
- Best of both worlds - Industrial reliability with custom flexibility
HTTP Dual Direction Pattern:
- Inbound HTTP for external system control and triggers
- Outbound HTTP for data publishing and integration
- Bidirectional integration with web-based systems
Multi-Protocol Recipe Strategy:
- Different recipes using different communication protocols
- Application-specific communication methods
- Protocol selection based on integration requirements
Protocol Translation and Bridging
Node-RED as Communication Bridge:
- Protocol conversion between different industrial systems
- Data format transformation for system compatibility
- Communication routing between multiple external systems
- Integration hub for complex multi-system environments
Communication Architecture Benefits
Design Advantages
Industrial Reliability:
- Native protocols provide immediate, reliable industrial communication
- Proven standards ensure compatibility with existing automation systems
Flexibility and Extensibility:
- Node-RED platform enables custom communication solutions
- Recipe-specific communication adapts to application requirements
- Future-proof architecture supports new protocols and integrations
Operational Efficiency:
- Multiple communication paths provide redundancy and options
- Real-time capabilities support high-speed production requirements
- Custom data processing optimizes information flow for specific applications